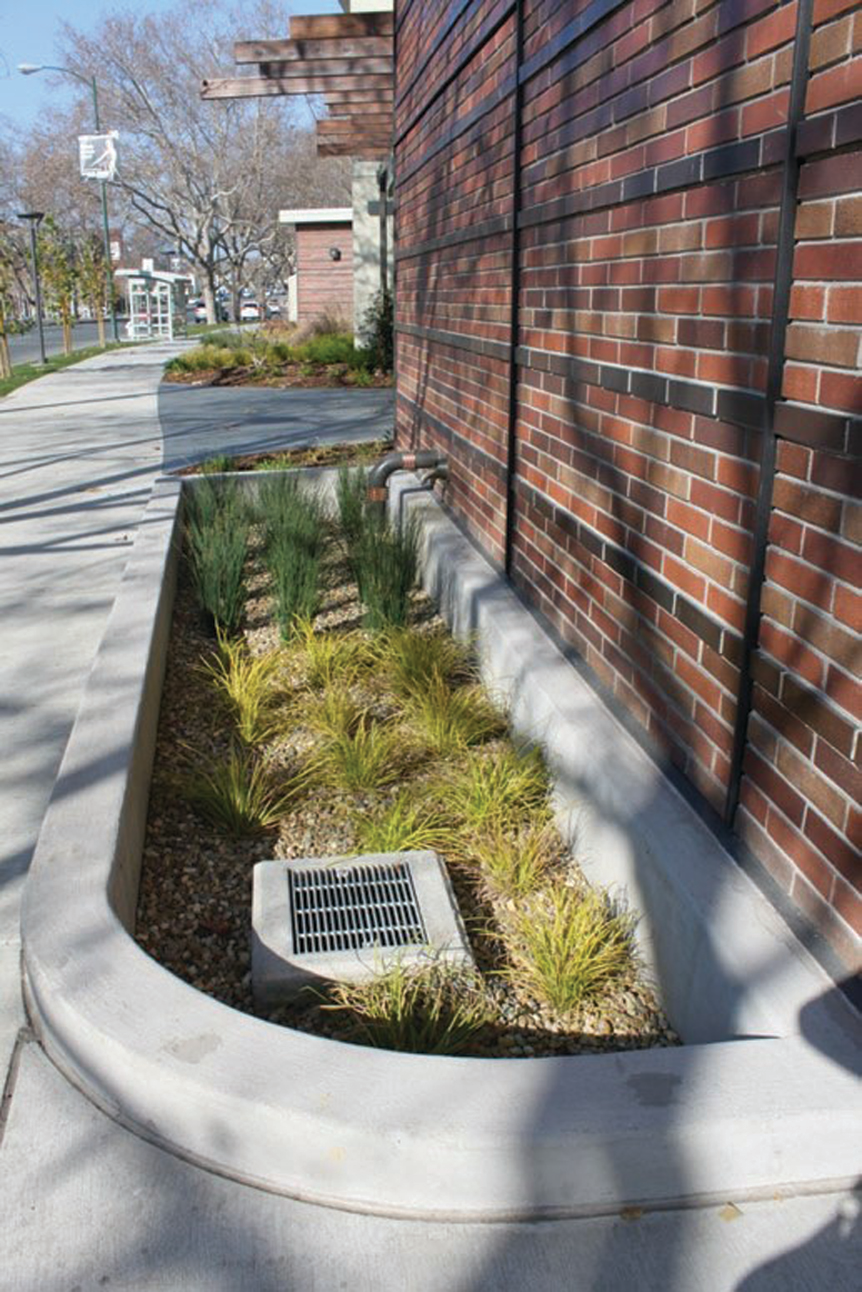
Flow-through planters are hard-edged stormwater management facilities with an impermeable base. Appropriate for infiltration-preclusive or high-density urban areas, flow-through planters treat water by allowing runoff to soak through its soil matrix and filter into an underdrain system.
Critical
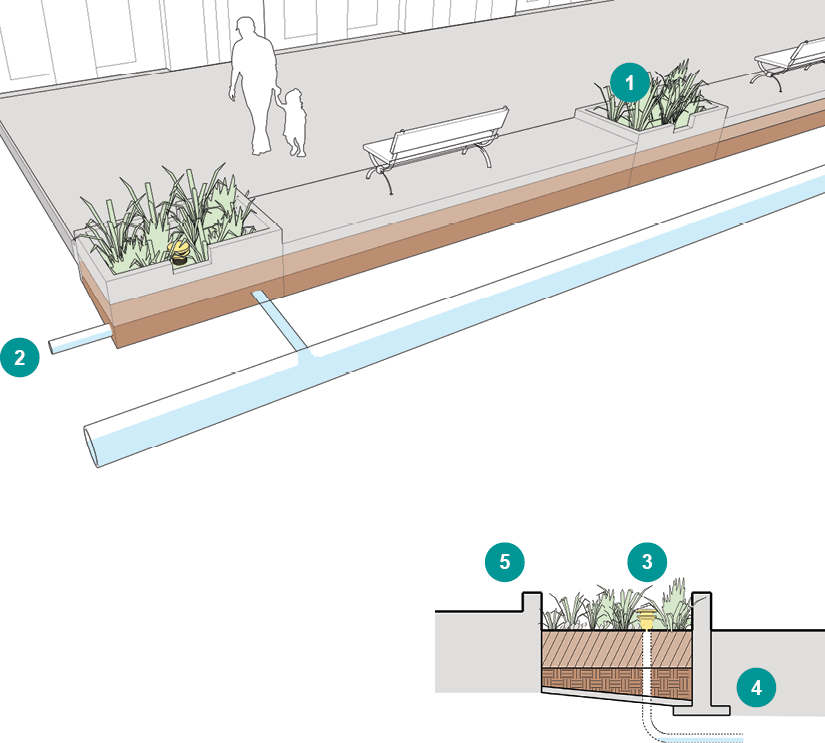
1Locate flow-through planters on non-infiltration areas, constrained sites next to buildings, areas with setback limitations, poorly draining soils, steep slopes (>4%), or areas with contaminated soils.
Use appropriate media composition for soil construction. The engineered soil mixture should consist of 5% maximum clay content.
2Install a perforated pipe at the base of the facility to collect the treated runoff.
3Use a raised drain to divert stormwater that exceeds the water quality event directly into drain system.
Install a downspout inlet or other conveyance sized for the water quality event and located to maximize treatment within the planter.
Provide a maximum 6-inch ponding depth for typical plant palettes. Deeper ponding depths require specialized planting palettes and should be avoided.
The drain rock layer must be clean and wrapped in filter fabric to protect the void space in the drain rock layer.
The planter must be designed to drain within 24 hours.
Recommended
Use native plantings that can handle seasonal flooding and require minimal irrigation.
Optional
4Structured footing may be needed given sidewalk or street conditions to prevent lateral movement of the walls of the flow through planter.
5Discourage pedestrian trampling and reduce soil compaction by using low barriers or hardy vegetative ground covers. Barriers may be designed into the planter structure as streetside seating.


Urban Street Stormwater Guide
Learn more about stormwater in NACTO’s Urban Street Stormwater Guide